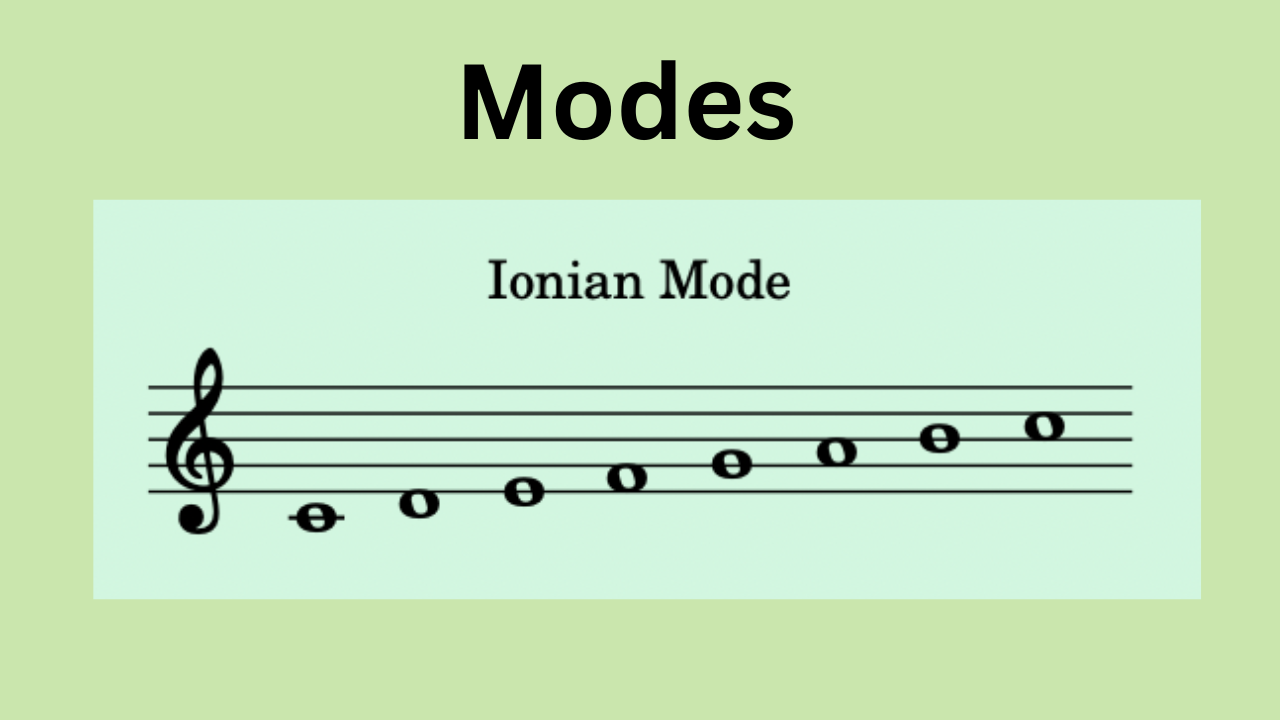
What Are Modes?
Music Theory Lesson: Exploring Musical Modes
Objective: To understand the concept of modes in music, their characteristics, and their application in various musical contexts.
Introduction to Musical Modes
Definition: Modes are scales derived from the parent major scale, each starting on a different degree of that scale. They have unique tonal qualities and are used to create different moods and atmospheres in music.
The Seven Modes
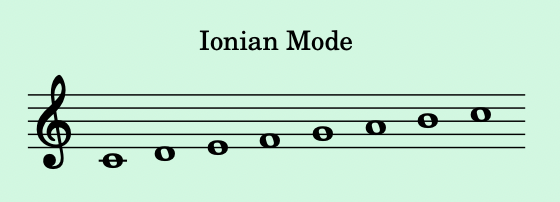
- Ionian Mode:
- Starts on the 1st degree of the major scale. It is essentially the major scale itself.
- Example: C to C on the C major scale:
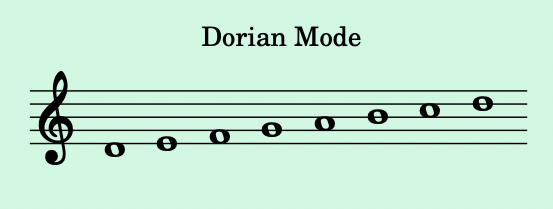
- Dorian Mode:
- Starts on the 2nd degree of the major scale. It has a minor feel with a raised 6th.
- Example: D to D on the C major scale:
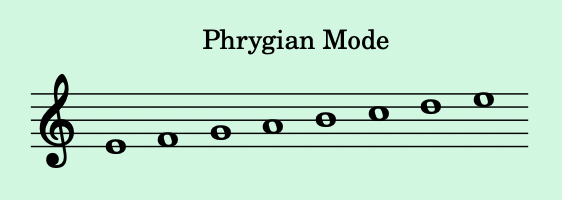
- Phrygian Mode:
- Starts on the 3rd degree. Known for its Spanish/flamenco sound, with a lowered 2nd.
- Example: E to E on the C major scale:
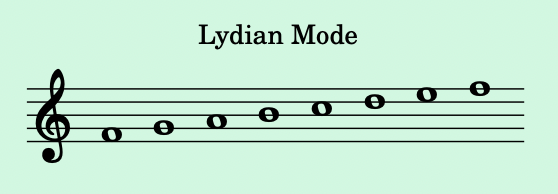
- Lydian Mode:
- Begins on the 4th degree. It has a major sound with a raised 4th, giving it a dreamy quality.
- Example: F to F on the C major scale:
- Mixolydian Mode:
- Starts on the 5th degree. It’s like a major scale but with a lowered 7th.
- Example: G to G on the C major scale:

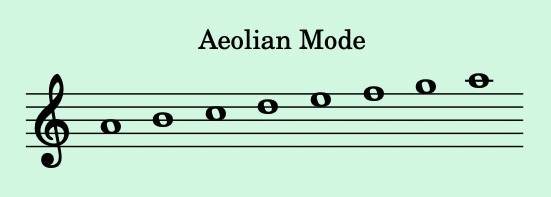
- Aeolian Mode:
- Begins on the 6th degree, also known as the natural minor scale.
- Example: A to A on the C major scale:
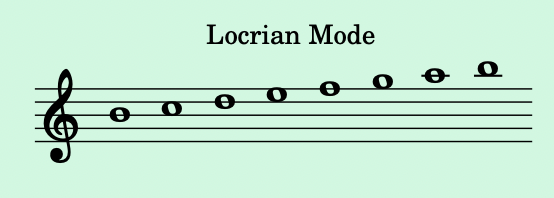
- Locrian Mode:
- Starts on the 7th degree. It has a diminished 5th and is rarely used due to its instability.
- Example: B to B on the C major scale:
Significance of Modes
- Musical Expression:
- Each mode has a distinct sound and feel, offering composers and musicians a wide palette for expression.
- Jazz and Folk Music:
- Modes are particularly significant in jazz and folk music for improvisation and melody construction.
- Modern Music:
- Many contemporary composers and songwriters use modes to create unique and innovative sounds.
Exercises
- Mode Identification:
- Practice identifying the different modes both visually on the staff and aurally.
- Improvisation:
- Improvise over simple chord progressions using different modes.
- Composition:
- Compose short pieces or melodies in various modes to explore their distinct sounds.
Conclusion
Understanding and using modes opens up a vast array of expressive possibilities in music. Each mode has its unique character, which can significantly influence the mood and atmosphere of a composition.
This lesson provides an introduction to musical modes, covering their characteristics and uses in music. Exercises are included to help musicians familiarize themselves with the sound and feel of each mode, enhancing their compositional and improvisational skills.